What is melanoma?
Melanoma develops from melanocytes (pigment cells). Melanoma usually occurs on parts of the body that have been sunburned. However, melanomas can sometimes start in parts of the skin or other parts of the body that have never been exposed to the sun. If detected early, most melanomas are curable.
If melanomas are not detected until later, they can become more serious.
A melanoma may appear as a new spot on normal skin, or develop from an existing mole. Melanomas usually begin as a flat spot that changes in size or shape or colour over months. While they remain flat they are generally curable. They usually remain flat for six to 12 months. Later, melanomas become bigger, irregular in shape and often darker in colour. A less common type of melanoma (called nodular melanoma) is not flat, but is raised from the start. These melanomas are often pink or red, and grow quickly. Not all melanomas are dark or black in colour.
Find out more about what causes melanoma.
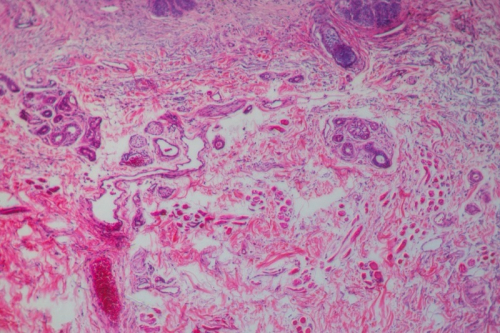
Cancer
Cancer is a disease of the body’s cells. Our bodies are always making new cells: so we can grow, to replace worn-out cells, or to heal damaged cells after an injury. This process is controlled by certain genes. All cancers are caused by changes to these genes.
Find out more about cancer
Skin
The skin has many important functions. It protects us from injury, cools us when we get too hot and prevents us from becoming dehydrated.
Find out more about skin
Skin cancers
Like all body tissues, the skin is made of tiny ‘building blocks’ called cells. These cells can sometimes become cancerous, for example under the influence of ultraviolet (UV) radiation.
Find out more about skin cancers
Melanoma
Melanoma develops from melanocytes (pigment cells). Melanoma usually occurs on parts of the body that have been sunburned.
Find out more about melanoma